Parameter Stores
Parameter Stores provide a new way to organize and manage parameters in your web or mobile app via the Statsig console. Now available for JS, React, React Native, Android, iOS, and Dart SDKs on the client side and java, node, python, and rust on the server side. Let us know in Slack if you'd like support in a certain language soon.
What is a Parameter Store?
Rather than thinking in terms of Statsig entities like Feature Gates, Experiments, Layers, or Dynamic Configs, Parameter Stores let you focus on parameters—the values in your app that need to be configurable remotely.
Parameter Stores decouple your code from configuration, indefinitely. This abstraction allows you to run experiments, adjust gating, or change values on the fly— without hardcoding any experiment/gate names. Instead you define parameters that can be remapped remotely to any value or any Statsig entity.
An Example: Parameterizing the Statsig Website
While usually release cycles are more painful on platforms like mobile, take the example of the Statsig Website - perhaps our marketing team asks for frequent updates, so we'd prefer to parameterize the text, images, buttons, colors and more:
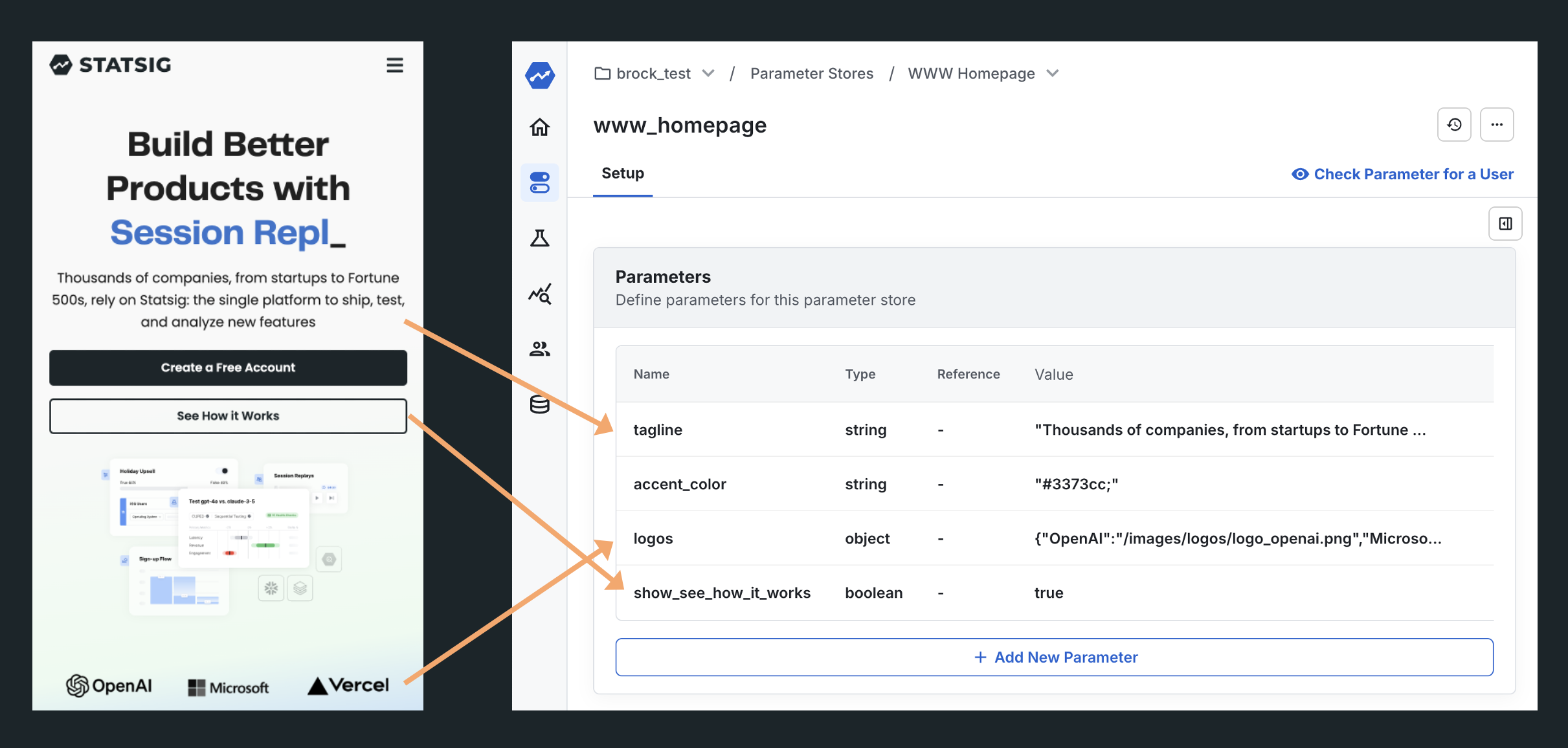
When the time comes to run an experiment, we can point these variables directly at experiments - starting an A/B test without writing a line of code:
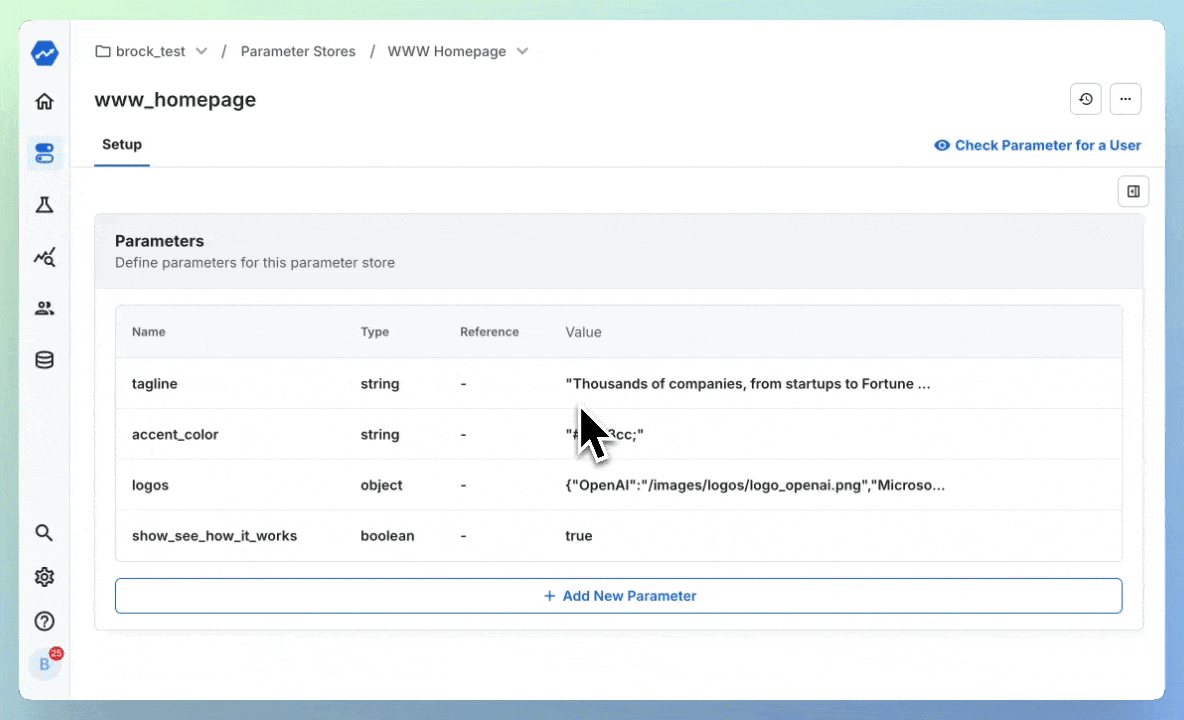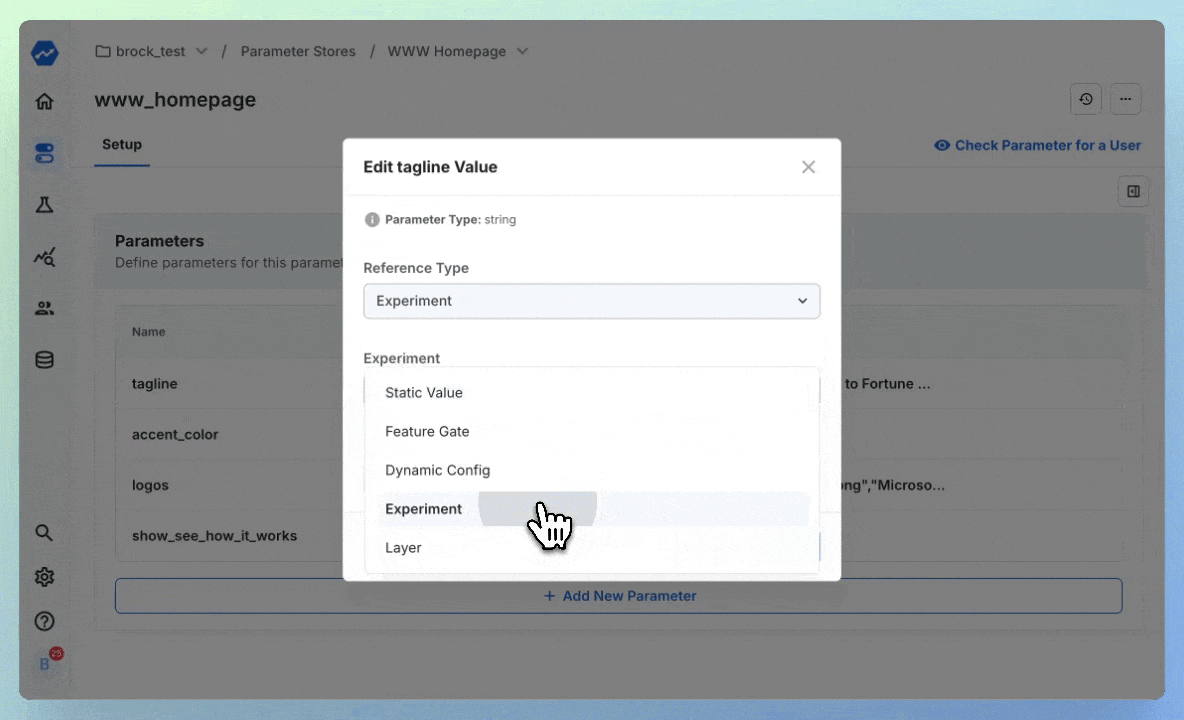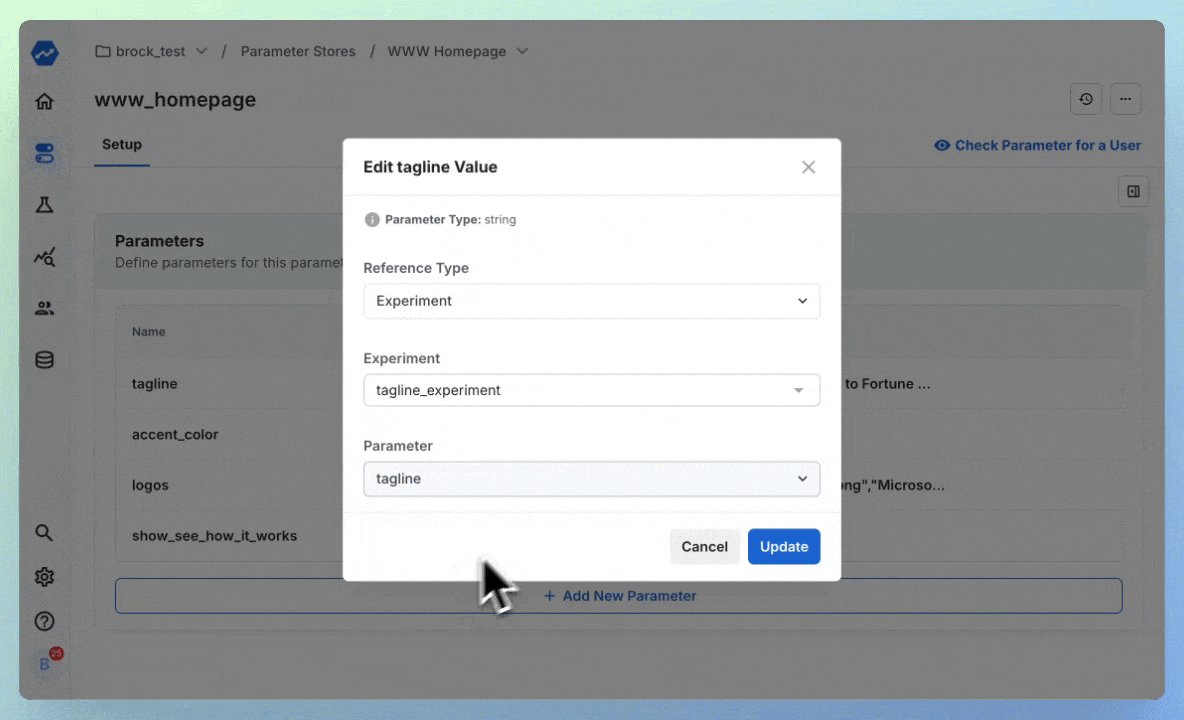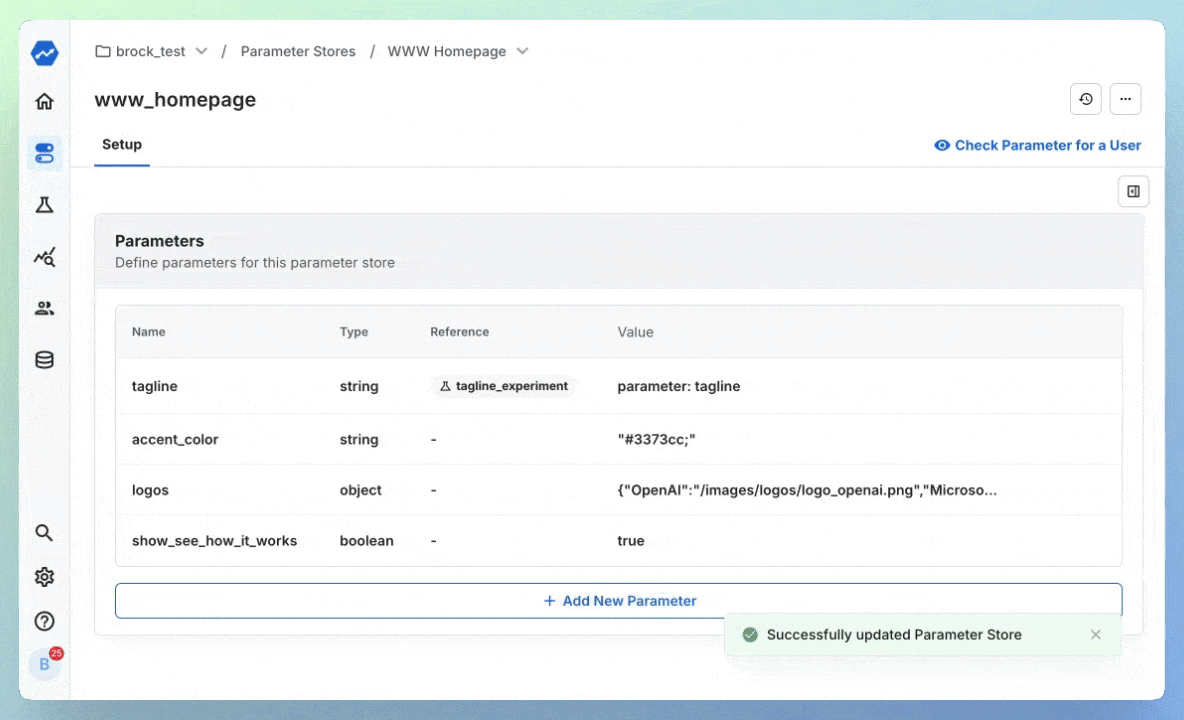
Now, you've begun an experiment on your tagline, without ever making a code change. You continue to access the parameter in-code like this:
const homepageStore = StatsigClient.getParameterStore("www_homepage");
const tagline = homepageStore.get("tagline", <optional_default_value>);
How to Use Parameter Stores
Here’s a suggested workflow:
-
Create a Parameter Store: Set up a Parameter Store for your team or project. Parameter Stores are designed to hold related parameters in one object.
-
Identify Configuration Variables: Consider which variables you want to decouple from your app and control via Statsig rather than hardcoding them in your app. These could include:
- A boolean parameter to control access to a new feature. Even if you're used to using Feature Gates for boolean feature management, start with a boolean parameter instead.
- A string parameter for text resources that you may want to swap or experiment with.
- A number parameter for inputs such as the number of onboarding steps, a list length to truncate, and more.
-
Start with Static Values: Begin with a static value for each parameter (what you would have hardcoded in the app). Use this static value initially.
-
Remap When Ready: Once your app is shipped and the feature is ready, remap the parameter to a Feature Gate, Experiment, Dynamic Config, or Layer. This allows you to test and target different variants.
-
Update in Real-Time: After experimenting, you can update the static value or gate the feature for specific app versions. This can be done in real time across mobile apps that are already released.
Why Use Parameter Stores?
If you’ve encountered this problem before, you’ll immediately recognize the power of Parameter Stores. For developers just starting with a Statsig SDK in their mobile apps, it’s beneficial to use Parameter Stores from the outset.
Parameter Stores are inspired by solutions like Facebook's Mobile Config, Uber's approach to experimentation, and Firebase Remote Config. These are used by leading mobile companies to:
- Move faster
- Maintain backward compatibility
- Experiment more freely
While the extra setup in the Statsig console may seem less convenient than creating a gate, it saves time later. Once your app version is shipped, Parameter Stores ensure that no Statsig entity values are hardcoded, giving you flexibility to update parameters without the need for a new release. This is particularly valuable for mobile apps, where app store release cycles create delays—unlike backends or websites, which can be updated quickly.
Supported SDK Versions
Parameter Stores are available in the following SDKs:
- Android SDK v4.33.0+
- iOS SDK v1.45.0+
- @statsig/js-client, @statsig/react-bindings, @statsig/react-native-bindings, @statsig/expo-bindings v1.4.0+
- Dart SDK v1.2.1+
- Statsig Server Core SDKs are gradually adding support, available in:
- com.statsig:javacore 0.1.0+
- statsig-rust 0.1.0+
- @statsig/statsig-node-core 0.1.0+
- statsig-python-core 0.5.0+
Parameter Stores will Not be available in non server-core server SDKs, nor available when Bootstrapping a client SDK from one of those sdks. Need support in a language soon? Let us know in Slack.